What’s Inside My Smartphone? — An In-Depth Look at the Components That Power Your Device
Cell phones are ubiquitous. We use them to communicate, to entertain ourselves, to work, and to learn. But do you know what makes a smartphone such a powerful device? What makes it tick?
Here you will learn about the most critical parts of a smartphone — the display, battery, camera, and sensors. Each part of your smartphone plays a vital role, and removing one will cause the device to malfunction.
1. Display — The Window to Your Digital World
Undoubtedly, the display is the most visible part of the smartphone. The display is the means through which we view photos, watch videos, read messages, and interact with countless applications.

Difference Between LCD, LED, and AMOLED Displays
Each of these technologies has its pros and cons in terms of clarity, brightness, and power consumption.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
- Uses back-light for illumination.
- Replicates color reproduction naturally.
- Bright in direct sunlight.
- Common in budget and mid-range smartphones.
LED (Light Emitting Diode) / AMOLED (Active Matrix OLED)
- Each pixel gets light (no back-light is needed).
- Stark contrast, vibrant color, deeper black.
- More power-efficient than LCD technology-can save battery AMOLED is activated for darker theme.
- Common in flagship smartphones of Samsung, OnePlus, and Apple.
In short: LCD = Bright and Natural, AMOLED = Deep and Vivid.
2. Battery — The Power Source That Keeps It All Running
A smartphone without a battery will always be a dull, useless device, a lifeless piece of glass and metal.
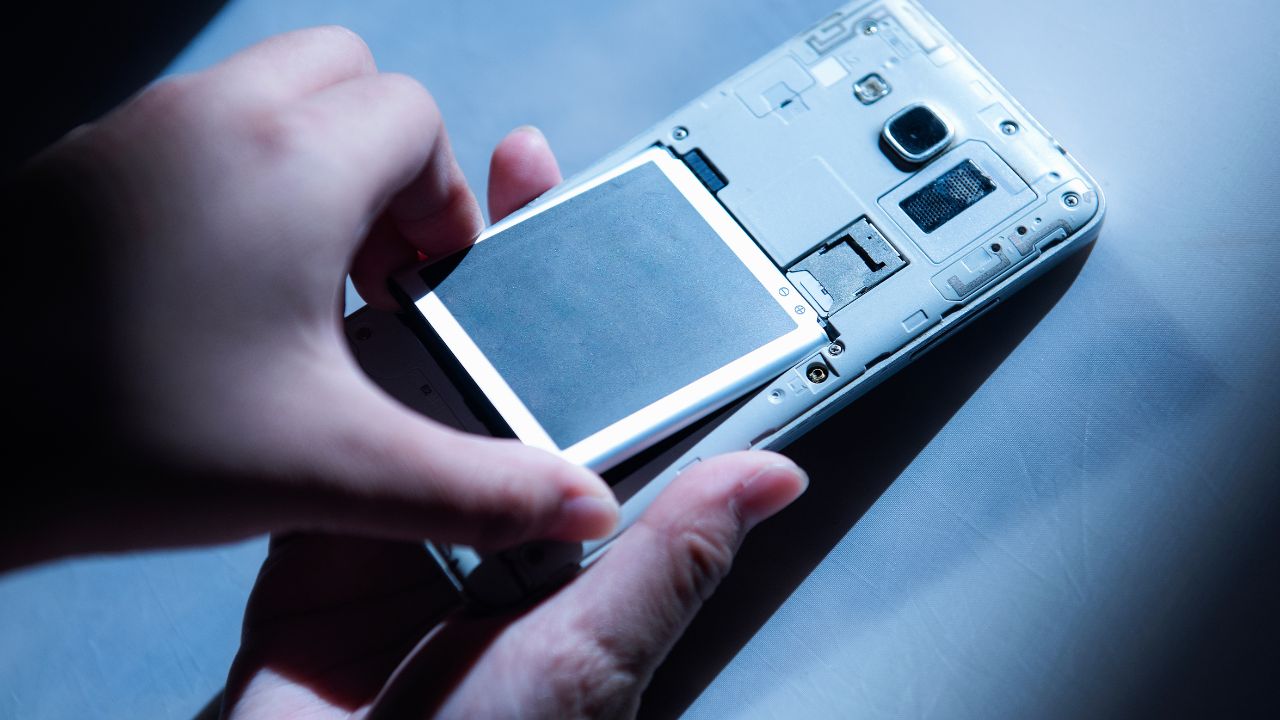

Lightweight and rechargeable, modern smartphone batteries take only a short amount of time to recharge and can be fully cycled hundreds of times before they lose the ability to hold a charge. Most modern smartphones, along with the rest of regions of the world, are powered with Lithium-ion (Li-ion) or Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) batteries.
Key Battery Factors:
Capacity (mAh): The higher the mAh, the longer the duration of battery life, but usage will always depend on the duration.
Fast Charging: Up to 50–70% charges completed in 30 minutes are possible with fast Charge technologies like Qualcomm Quick Charge, USB Power Delivery or other proprietary fast chargers.
Battery Optimization: Newer systems on chips (SoC) with integrated processors and other software like Android’s Adaptive Battery improve battery life by reducing the background processes.
There are fast charging technologies in the market now. The smartphone charging can be done in less than 10 minutes. This means, the smartphones of the future can be powered with graphene batteries.
3. System-on-a-Chip (SoC) — The Brain of Your Smartphone
SoCs (System-on-Chip) propelled the transformation of mobile phones into smartphones. SoCs allows for the integration of the mobile CPU, GP, modem, and AI into one single unit.
SoC Components:
CPU (Central Processing Unit): Executes system and application instructions. Example: ARM Cortex command processors.
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Visual rendering which is important during games and animations.
AI/Neural Engine: Voice command, image improvements, and predictive text are some of the tasks handled.
Modem: Controls the 4G/5G network access.
4. Memory and Storage — Where Your Data Lives
There are two main types of memory for smartphones: RAM and ROM (storage). Both of these are critical for the efficiency and speed of your smartphone.
RAM (Random Access Memory)
It is temporary memory which is used for the currently running processes and apps. The smartphone can multitask better with higher RAM. Typical RAM sizes are 4GB, 6GB, 8GB, and flagship models can go as high as 16GB.
Storage (Internal Memory)
It contains system files, apps, and media. Higher end smartphones use the UFS technology for internal memory, while budget ones use the slower eMMC. Some smartphones use microSD cards for additional storage.
Your smartphone can run smoothly, and perform faster, with a well-balanced RAM and UFS storage.
Some popular smartphone SoCs are Qualcomm Snapdragon, Apple A-series, MediaTek Dimensity, and Samsung Exynos.
In short, an SoC is your smartphone’s entire computer on a chip, as it controls the performance, power efficiency, and user experience.
5. Modems — Your Gateway to Connectivity
Your smartphone modem is your link to the digital world. It manages your mobile data (4G, 5G), calls, SMS, and internet access.
Modems translate data between your carrier’s network and your phone. Modern modems also support multiple network bands for global roaming. In 5G phones, Snapdragons X70 or MediaTek M80 modem offers ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and improved signal consistency.
Modems have advanced from 3G to 4G to 5G and now, high-definition video streaming, cloud gaming, and video calls can be joined seamlessly at any time or place.
6. Camera — Capturing Life in Pixels
Most people buy phones based on the camera performance, as it is considered to be one of the most important component of a smartphone. A smartphone camera is not just a lens, but a combination of hardware and software.

Camera Hardware:
Lens: Captures light and focuses it onto the sensor.
Light Conversion to Digital Signals And Sensor Size
Larger sensors convert more light, giving better performance in low-light situations.
Aperture
A camera’s aperture controls how much light enters. How much light is allowed is captured in f-number.
Optical Image Stabilization
Optical Image Stabilization helps remove blur in pictures taken in unsteady conditions.
Software
Color and sharpness enhancement, high dynamic range imaging, and other edge cutting tools are part of software.
AI
AI also improves portrait mode, scene optimizations, and face detection.
More lenses are being integrated into high-tier smartphones. Having wide, ultra-wide, telephoto, and macro lenses, depth sensors and providing professional pictures has become handy.
7. Sensors – The Meaning of ‘Smart’
You can sense the world due to tiny components in your phone.

Mobile Device Parts that sense the environment
Most smartphones have these parts:
- Accelerometer: used in screen rotation.
- Gyroscope: used for advanced motion sensors.
- Proximity Sensor: Turns screen off to save battery.
- Ambient Light Sensor: Turns off the screen and saves battery.
- Fingerprint Sensor: Detects people to unlock phones.
- Magnetometer: Physical world navigation.
- Barometer: Measures changes in air to assist GPS.
All these parts, combined, give more capabilities and make a phone smarter.
Integration of Hardware and Software
Each of these parts — screen, system on chip, memory, camera, sensors, and battery — coordinates under an operating system, whether Android or iOS.
Mobile operating systems serves to streamline communication between different hardware functionality and to optimize CPU and battery resource distribution to facilitate a user experience that is as seamless as possible.
Android and iOS smartphones come with user-centric AI smartphone optimizers, which help to improve photo quality, manage to close unnecessary apps, and even extend battery life based on the user’s habits.
Integration of New Smartphone Technology
Foldable screens are now a reality. Other innovations include:
Batteries that use graphene and can be charged quickly, system on chip combined with AI, and under-display cameras.
Mobile sensors are now able to monitor and measure health and smartphones are expected to get even more powerful and energy efficient with self-charging capabilities.
Do Smartphones Improve Technology
Smartphones are a result of advanced mobile technology. When you smartphones, think of me and the modern technology that has made it possible. It is a result of advanced mobile technology.
Smartphones are a result of advanced mobile technology. When you smartphones, think of me and the modern technology.What makes a smartphone a supercomputer that fits into a pocket? Knowing what goes into a smartphone makes us appreciate its greatness much more.




